Real-time data and the growing importance of data in general are changing the way we collect and interact with information. A host of hardware and software innovations are pushing connectivity beyond today’s limits1.
In businesses, we connect and link an increased number of devices, sensors and systems to networks designed to collect and share data. This allows us to monitor and control information according to its anticipated interaction within those networks.
This connectivity gave rise to related terms such as digital transformation, Internet of Things (IoT), connected objects and Industry 4.0, which are often confused with one another. Companies are interested in 4.0, but few are equipped and capable of effectively reaching this goal.
In a nutshell, 4.0 is achieved by showcasing the interoperability of various systems thanks to a multitude of useful data. It’s a mindset where the objective is to connect related systems through data sharing. While the use of connected devices is essential, there’s a bit more to it than that. What’s important is to visualize and understand the scope of data dynamics in your processes.
Understanding how to achieve Industry 4.0 status involves paying attention to data dynamics and real-time information flowing through your company systems.
Why Industry 4.0
It’s called Industry 4.0 simply because it’s the “Fourth Industrial Revolution,” but it’s more than just a buzzword. In fact, the disturbances caused by this phenomenon continue to affect several industries. This so-called Fourth Industrial Revolution is characterized by a slow but radical societal transformation, so it may be too early to call it a full-on revolution.
In hindsight, we can conclude that these innovations were in fact achieved out of a desire to improve process management thanks to the technological innovations available at the time.
In Quebec, the adoption of Industry 4.0 has proven to be difficult for many companies, and the road ahead is clouded with uncertainty. Before we delve further into the topic, let’s quickly summarize the evolution of the manufacturing sector and its reliance on data and connectivity over the past few years.
The First Industrial Revolution (1750~1840) marked the rise of mechanization powered by steam and water. The electrification of equipment, which made mass production possible, gave way to the Second Industrial Revolution (1870~1914). This was followed by the Third Industrial Revolution (1960~2000), which was characterized by advancements in digitization through the use of computers.
As for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, it began in Germany (2011~2016) following the adoption of a government initiative to promote emerging technologies in the manufacturing industry. The goal was to foster the digitization of manufacturing processes using cutting-edge technologies.
How we evolved from 3.0 to 4.0
Since computers and digitization are still very much part of today’s world, you may be wondering how we went from 3.0 to 4.0. The main differences can be found in the management of information and a system’s capabilities/power.
Connectivity and interoperability have allowed us to link the digital and physical worlds through smart objects and connected systems. The scope of this connectivity enables cooperation through information transparency across the entire network. This collaboration exponentially increases the volume of information and our ability to make real-time decisions, even in a decentralized and autonomous manner.
Still not convinced? Consider the old inventory management method used by manufacturing companies where an employee with a hand-held scanner was given the task of scanning production-floor shelves and even entire warehouses. The purpose was to update the inventory management system based on what was available on site.
Today, there is no need for all this hassle, as cameras and even drones have taken over the task. These devices generate real-time video streams which, once analyzed, allow production systems (MES, ERP, PLM, WMS, etc.) to track inventory and location without human intervention.
Removing human input increases the accuracy of inventory management systems, creating a solid foundation and providing a better view of current, future, and consumable assets. Throw in a few autonomous robots to manage the inventory, and you have a great example of Smart Manufacturing as outlined by Cedric in this blog post.
How to successfully become Industry 4.0
First, you need a game plan. The story behind our colleague Jean-Sébastien’s company is a case in point! In manufacturing, we often find departments and systems working in silos where information is created, stored, and disposed of independently from one another. These environments create micro-ecosystems that add little or no information to the overall picture required to manage a business properly.
Creating a successful 4.0 ecosystem involves a few important steps:
- Devising a plan that determines the scope of the ecosystem and the various systems relevant to its functioning
- Establishing the type and structure of the network through which the information will flow
- Understanding the various types of connected objects linked on this network as well as their ability to form the IoT and contribute to the flow of information
- Initiating connectivity from the equipment to your data warehouse while avoiding the opposite.
These steps help narrow down the scope of connectivity required to achieve your 4.0 goals. In fact, this last point is crucial to identify each area where the informational potential of collected raw data is enhanced by related systems in the ecosystem. As the informational potential increases, so does our decision-making capabilities!
A typical integration often looks like this:
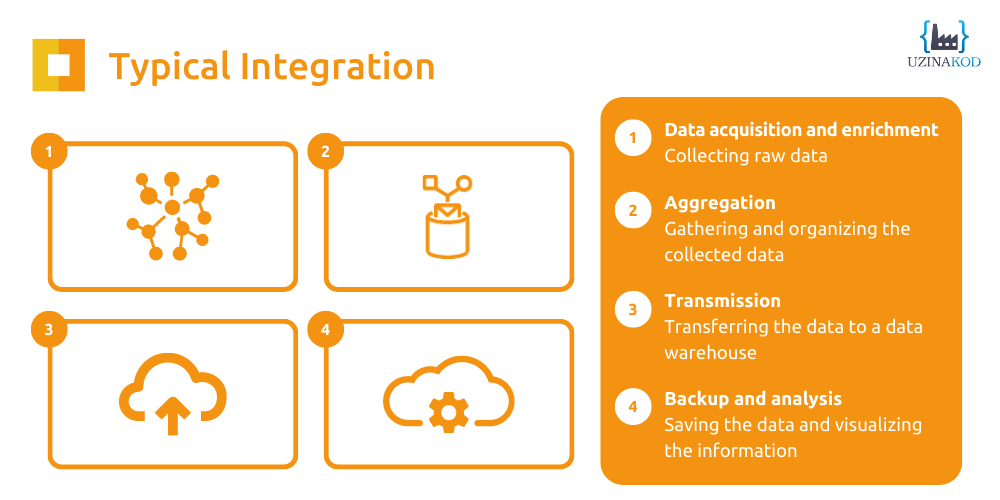
Data acquisition, aggregation and transmission are processes that are usually carried out at the factory floor level. Backup and analysis occur in data warehouses because these infrastructures are able to process huge amounts of information, make decisions in real time, centralize the information and define the resulting actions according to the collected data.
Conclusion
As you can see, bringing your industry into the 4.0 era is no easy task. Given the array of emerging technologies, it’s difficult to predict which ones will prevail and which trends will be adopted and integrated by a vast majority of companies.
Your business goals should be at the heart of your 4.0 projects, but it’s crucial to begin slowly and gradually increase the level of complexity. One-size-fits-all solutions simply don’t exist.
Taking advantage of automation to maximize the high-potential data found in your processes will allow you to evolve. Your business will benefit from this essential data enhancement, which is highly recommended when managing processes.
As Microsoft and Databricks partners, Uzinakod is able to assist you with the development of Industry 4.0 solutions. Contact us now to discuss your goals.
1Rousseau, F., Wong, T. (2022). IoT Messaging using Low-Cost COTS Devices, 7th International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Orlando, Florida, June 12-14, paper ID 265, ISSN: 2169-8767



